SPE1.1.0.2
FILES AND FOLDERS DESTRUCTION

CONTENTS
- Summary
- Choice destruction method
- Selected files and folders destruction
- Destruct files in package
- Destruction audit report examples
SUMMARY
File destruction is the process of removing files from the device on which they are stored in a way that prevents them from being recovered even if specialized hardware and software are used for this purpose.
File Destroy Manager (FDM) uses both standard file destruction algorithms and hybrid solutions that are based on combinatorial and cryptographic methods, as well as special-purpose auxiliary processes.
In the standard versions of the application, two basic methods of destruction of files and directories are included as follows:
- Destruction of selected files and directories (operational method) - Only those files and directories marked for deletion in Shell List panel are destroyed;
- Destroy files and directories whose metadata is written in the file packages (batch method) - Files and directories for which data is available in the file bundle and which are physically accessible regardless of whether they are located on local, server or mobile devices are destroyed.
Note: In enterprise versions of the application, a method is also available in which the data is destroyed in secure container files (**). Working with this method requires a completed certification course in the Black Screen curriculum.
CHOICE DESTRUCTION METHOD
The choice of method determines the ratio of execution time / guarantee of the result of the destruction process. The more reliable the method, the more time required to perform the processes.
The choice in which we are guaranteed to get the best result in the shortest time is considered optimal.
In standard methods, the security is a function of the number of repetitions of the actions performed. This means that a higher security will only be guaranteed by a larger number of repetitions, which leads to a longer execution time interval. This necessitates the use of hybrid solutions that guarantee a high degree of security for much shorter time intervals. The difference between them and the standard methods is the presence of crypto processes as well as auxiliary functions that perform specific transformations.
Destruction of the selected data will be done using the combination of standard and hybrid methods. Before starting the file and package destruction procedure, a warning message will be displayed, unless its appearance has been previously canceled.
In the standard versions, once the process has been started, it cannot be canceled in any way. In enterprise solutions, there are various functions and settings that allow suspending and/or temporarily interrupting the process.
The deletion method is selected by selecting File - Delete method from the main menu, as shown in the image below.

Fig.1. Choice destruction method.
- Securе - The technology used meets the requirements of The Department of Defense Standard 5220.22-M. The method guarantees high speed and a relatively good level of protection.
- DoD - The technology used meets the requirements of The Department of Defense Standard 5220.22-M and NIST Publication 800-88. The method guarantees very good protection at optimal speed.
- NSA - The algorithms used meet the requirements of the NSA's Center for Storage Device Sanitization Research (CSDSR) and sanitization of information system (IS) storage devices. The method guarantees very good protection at optimal speed.
- Gutmann - The Gutmann method is an algorithm for securely erasing the files and folders. It achieves a complete erase of the disk contents by repeatedly writing 35 segments in the sectors to be erased.This is the most thorough erasing standard method, but it also takes a long time due to the multiple erasing times.
- BS Standard - Hibrid algorithm for securely destroing files and folders. In addition to erasing the data, a preliminary conversion of the files is performed, which uses cryptographic primitives combined randomly.
- BS Ultra - Hibrid algorithm for guaranteed destroing files and folders. It allows overwriting at the bitwise level, with the sector length being chosen randomly and not always is an even number. It uses an extended set of cryptographic primitives including modified KDF-functions. In the corporate versions of the application, control strings and other non-standard solutions specific to FPS are used.
Note: By default, the application uses DoD (medium security) method combined with BS Ultra Hibrid Algorithm.
SELECTED FILES AND FOLDERS DESTRUCTION
Destruction of selected files and folders or so-called "operational destruction" applies only to those files and folders that are visible (accessible) in Shell LIst panel.
Destruction of the selected data will be done through the pre-selected combination of standard and hybrid methods. A warning message will be displayed before the files and folders destruction procedure begins. If the destruction is not confirmed, the process will be terminated without affecting the selected files in any way.
In the standard versions, once the process has been started, it cannot be canceled in any way. In enterprise solutions, there are various functions and settings that allow suspending and/or temporarily interrupting the process.

Fig.2. Selected files and folders destruction process.
In this case, the check box Delete files in package must be disabled, as shown in the image below. This ensures that the application will work as a file manager and will not process the information stored in the packets.

Fig.3. Selected files and folders destruction process.
To start the shredding process, you can click on the Shredding button located on the system panel or use the Shift+Del keyboard shortcut.
Before the process starts, a final confirmation will be requested from the user to perform the indicated actions.
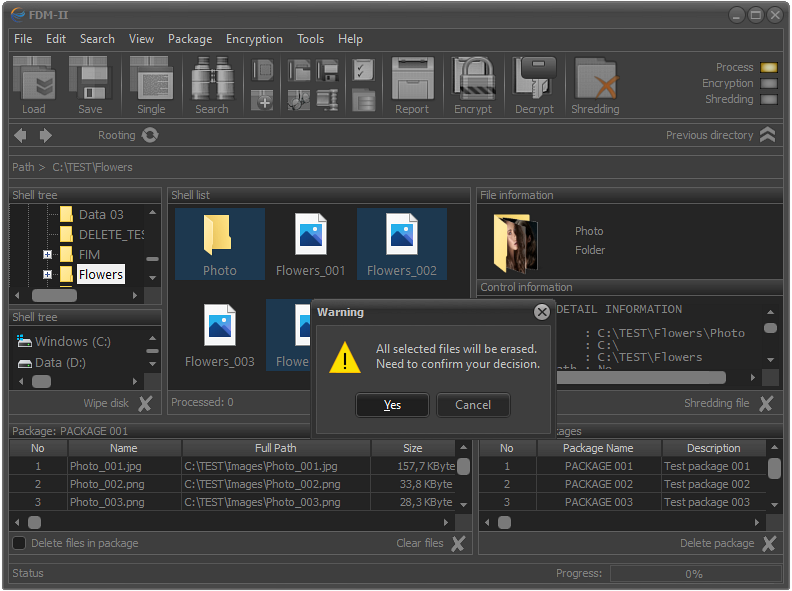
Fig.4. Warning that the selected files and folders will be destroyed.
The results of the execution of the process will be visualized in real time in the Status bar panel.
When the process is finished in the Shell list panel, the current status of the selected directory and/or drive will be displayed. This means that deleted files and folders will not be listed.

Fig.5. The list of files and directories after destruction.
The results of the destruction process will be recorded in the system report. This includes information about the deleted files and folders, their parameters, the duration of the process, etc.
To create system report, you can click on the Report button located on the system panel or use the Ctrl+P keyboard shortcut.

Fig.5. Selected files and folders destruction control report.
DESTRUCT FILES IN PACKAGE
Destruction of the files in selected package or so-called "package destruction" is the physical destruction of all accessible files and folders for which meta information is available in the package.
In this case, all accessible files and folders that can be physically accessed are subject to destruction, regardless of whether they are locally located, whether they are stored on a file server or are an element of another type of network resources or they are saved on an external disk or mobile device.
In this case, the files and directories that are subject to destruction may not be visible in Shell list. The only thing that matters is that the information about them is contained in the package and there is guaranteed physical access to the device where they are stored.

Fig.6. Destruct files in package.
In this case, the check box Delete files in package must be enabled, as shown in the image below. This ensures that the application will work as a package manager.

Fig.7. Destruction files in package process.
A warning message will be displayed before the files and folders in selected package will be destruction procedure begins.

Fig.8. Destruction files in package process.
Destruction of the selected data will be done through the pre-selected combination of standard and hybrid methods.
DESTRUCTION AUDIT REPORT EXAMPLES
Each of the audit reports containing data about the file destruction process can be converted to some of the most commonly used electronic document formats.
The examples below give an idea of how standard reports should look. It is also possible to display reports in .DOC, .DOCX and .XLS, XLSX format, but for this the user is required to have a licensed MS Office.
Note: In the corporate versions of the product, the reports are prepared at the customer's request and may include non-standard information.
Contents